

Contact +57 3184190900
The following list is sorted by course and contains detailed relevant projects and practical classes developed during the degree of Mechatronics Engineering in Nueva Granada Military University.
©All rights reserved to the intelectual authors mentioned on each paper.
Year: 2016 | Engineering fields: Power electronics | Technology brands: LabVolt Festo (Motor & Dynamometer) | Keywords: Winding motor, Power, Load, Torque, Magnetic field
Year: 2016 | Engineering fields: Power electronics | Technology brands: LabVolt FESTO (Motor & Dynamometer) | Keywords: Winding motor, Power, Load, Torque, Field current, Core current, Parallel connection
Year: 2016 | Engineering fields: Power electronics, Analog and Digital electronics, Microcontrolelrs, Embedded, Programming and simulation | Technology brands: LabVolt Festo (Motor & Dynamometer), ST (Microcontroller) | Keywords: Motor, Power, Load, Torque, Field current, PWM-Pulse Width Modulation, Safe electronics, Optocoupler
Year: 2016 | Engineering fields: Power electronics, Programming and simulation | Technology brands: LabVolt Festo (Motor & Dynamometer) | Keywords: Motor, Power, Load, Torque, Delta connection, Star connection
Year: 2016 | Engineering fields: Power electronics, Analog and Digital electronics, Microcontrolelrs, Embedded, Programming and simulation | Technology brands: YASKAWA (Servomotor AC), ST (Microcontroller) | Keywords: Servomotor, Rated speed, Pulse train, Position control, Speed control
Year: 2016 | Engineering fields: Pneumatics, Programming and simulation | Technology brands: FESTO (Pneumatics kit), Fluidsim (FESTO Simulation software) | Keywords: Pneumatic sequences, Valves, Force and speed analysis, Intuitive method, Cascade method
Year: 2016 | Engineering fields: Pneumatics, Programming and simulation | Technology brands: FESTO (Pneumatics kit), Fluidsim (FESTO Simulation software) | Keywords: Pneumatic sequences, Valves, Force and speed analysis, Pneumatic counter, Pneumatic timer
Year: 2016 | Engineering fields: Pneumatics, Programming and simulation | Technology brands: FESTO (Pneumatic and electric kit), Fluidsim (FESTO Simulation software) | Keywords: Electropneumatic sequences, Valves, Force and speed analysis, Pneumatic counter, Pneumatic timer, Relays
Year: 2016 | Engineering fields: Hydraulics, Programming and simulation | Technology brands: FESTO (Hydraulic and electric kit), Fluidsim (FESTO Simulation software) | Keywords: Hydraulics, Valves, Force and speed analysis, Hydraulic applications
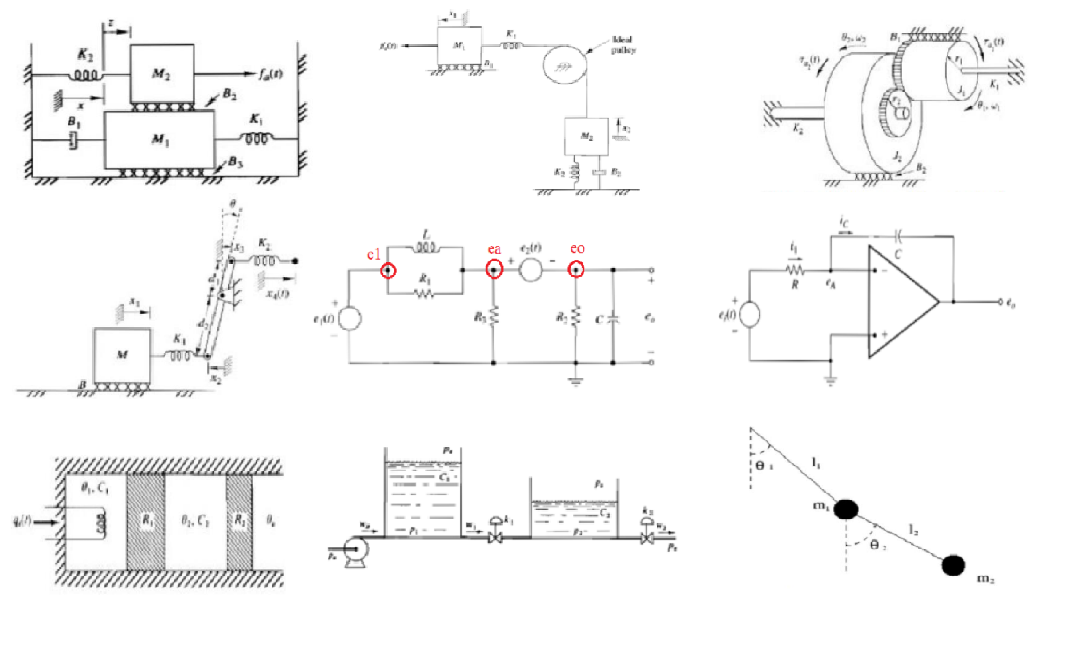
Year: 2017 | Engineering fields: Control and signal processing, Mathematics and Physics, Statics & Dynamics, Programming and simulation | Technology brands: Matlab & Simulink (Simulation software) | Keywords: Mechatronics modelling, Newton-Euler, Euler-Lagrange, Open-loop response, Translational mechanical system model, Rotational mechanical system model, Electrical system model, Liquid level system model, Thermal system model, Hydraulic system model
Year: 2017 | Engineering fields: Control and signal processing, Mathematics, Programming and simulation | Technology brands: Matlab & Simulink (Simulation software) | Keywords: Mechatronics modelling, Newton-Euler, Euler-Lagrange, Open-loop response, Proportional control, Derivative control, Integral control, PID control, Second order control
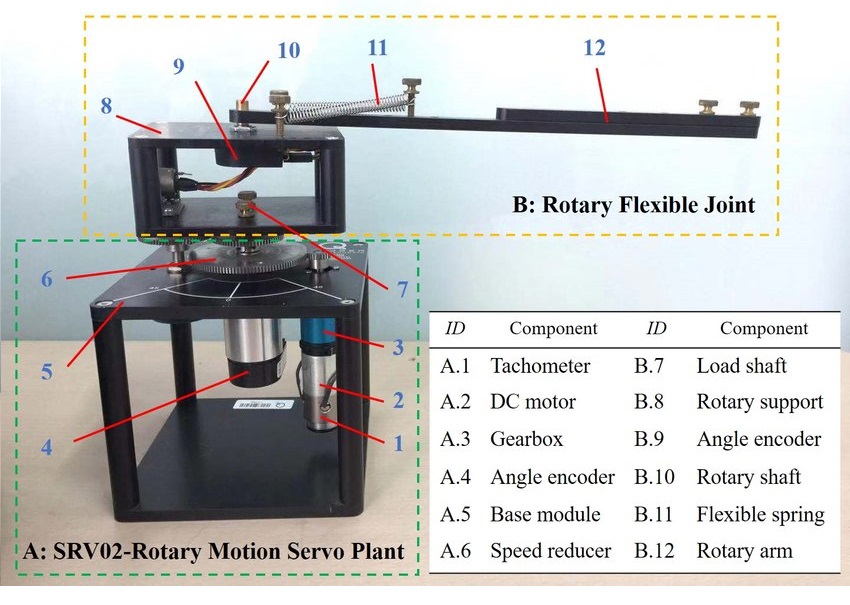
Year: 2017 | Engineering fields: Control and signal processing, Analog electronics, Design, Programming and simulation | Technology brands: Matlab & Simulink (Simulation software) | Keywords: Mechatronics modelling, Newton-Euler, Euler-Lagrange, Proportional control, Derivative control, Integral control, PID control, Second order control
Year: 2017 | Engineering fields: Control and signal processing, CAD, Mathematics, Electronics, Programming and simulation | Technology brands: Matlab & Simulink (Simulation software) | Keywords: Mechatronics modelling, Newton-Euler, Matlab PIDTool, Transfer function, Push and Pull circuit
Year: 2017 | Engineering fields: Control and signal processing, Mathematics, Programming and simulation | Technology brands: Matlab & Simulink (Simulation software) | Keywords: Mechatronics modelling, Space state model, Observer, Linear system, Nonlinear system, Transfer function
Year: 2017 | Engineering fields: Control and signal processing, Analog electronics, Mathematics, Programming and simulation | Technology brands: Matlab & Simulink (Simulation software) | Keywords: Mechatronics modelling, Frequency compensation control, Lead compensator, Phase and Gain margin, Linear system, Transfer function
Year: 2017 | Engineering fields: Control and signal processing, Analog electronics, Mathematics, Programming and simulation | Technology brands: Matlab & Simulink (Simulation software), LabView National Instruments (DAQ system) | Keywords: Mechatronics modelling, continuous control, Discrete control, Digital-Analog converter, Linear system, Transfer function, Position control
Year: 2017 | Engineering fields: Control and signal processing, Analog electronics, Embedded, Programming and simulation | Technology brands: Matlab & Simulink (Simulation software), Arduino (Embedded device) | Keywords: Mechatronics modelling, continuous control, Discrete control, Digital-Analog converter, Microcontroller, Transfer function, Serial communication, Position control
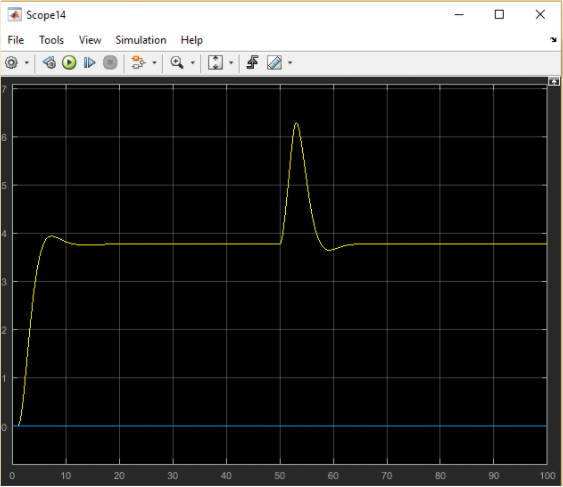
Year: 2017 | Engineering fields: Control and signal processing, Mathematics and Physics, Statics & Dynamics, Programming and simulation | Technology brands: Matlab & Simulink (Simulation software) | Keywords: Mechatronics modelling, Space State, Observer, Disturbances, Canonic form, Controllable canonical form, Observable canonical form
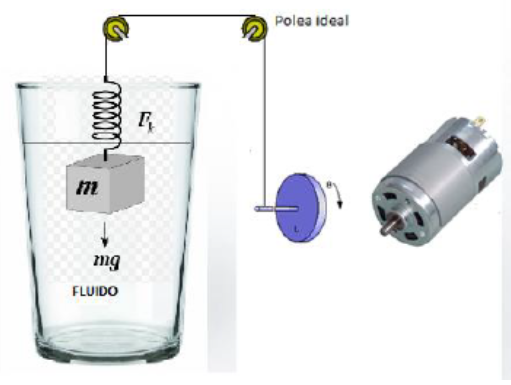
Year: 2017 | Engineering fields: Control and signal processing, Mathematics and Physics, Statics & Dynamics, Programming and simulation | Technology brands: Matlab & Simulink (Simulation software) | Keywords: Mechatronics modelling, Transfer function, Open loop, Feedback, Hall effect sensor
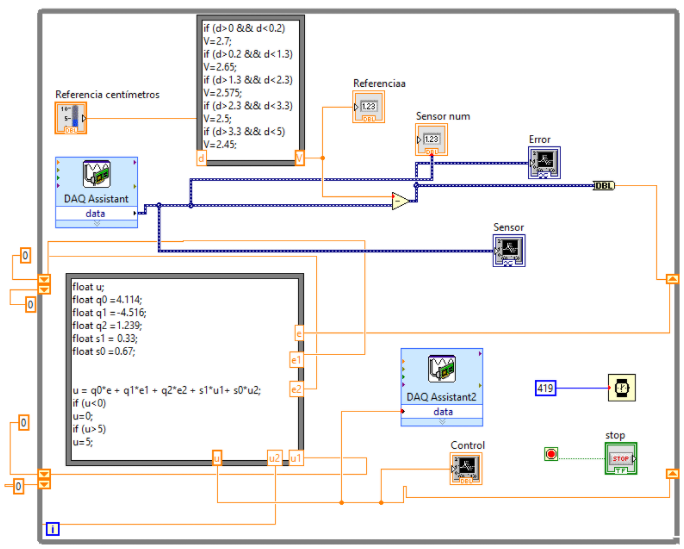
Year: 2017 | Engineering fields: Control and signal processing, Mathematics and Physics, Programming and simulation | Technology brands: Matlab & Simulink (Simulation software), LabView National Instruments (DAQ system) | Keywords: Mechatronics modelling, Transfer function, Root locus control, Frequency compensation, Pole/Zero cancellation control, Oscillation death control, Discrete servosystem
Year: 2017 | Engineering fields: Control and signal processing, Mathematics and Physics, Programming and simulation | Technology brands: Matlab & Simulink (Simulation software) | Keywords: Mechatronics modelling, Transfer function, Space state control, Furuta pendulum,
Year: 2018 | Engineering fields: Analog and Digital electronics, Control and signal processing, Programming and simulation | Technology brands: Fischertechnik (Factory 4.0 assembly), Fluidsim FESTO (Simulation software) | Keywords: Characterization, Digital electronics, Analog electronics, Fischertechnik
Year: 2018 | Engineering fields: Analog and Digital electronics, Control and signal processing, Programming and simulation | Technology brands: Siemens (PLC S7-1500), TIA PORTAL Siemens (Software), Automation Studio (Connection software) | Keywords: Characterization, Digital electronics, Analog electronics, Automation, Siemens, Portal, Ladder language, SCL
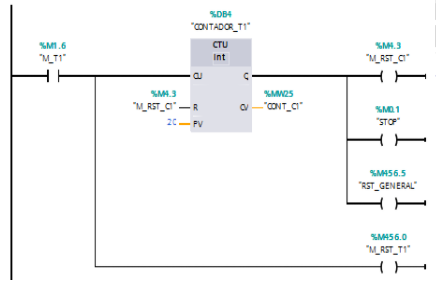
Year: 2018 | Engineering fields: Analog and Digital electronics, Control and signal processing, Programming and simulation | Technology brands: Siemens (PLC S7-1500), TIA PORTAL Siemens (Software), Automation Studio (Connection software) | Keywords: Characterization, Digital electronics, Analog electronics, Siemens, TIA Portal, Hydraulic cylinders
Year: 2018 | Engineering fields: Analog and Digital electronics, Control and signal processing, Mechanics, Programming and simulation | Technology brands: Siemens (PLC S7-1500, Micromaster 440, Motor 1LA7 070 2YA60), TIA PORTAL Siemens (Software), YASKAWA (Servomotor), Automation Studio (Connection software) | Keywords: Characterization, Digital electronics, Analog electronics, Siemens, TIA Portal, Hydraulic cylinders, Variable speed drive, Micromaster 440, PROFIBUS, Yaskawa

Year: 2018 | Engineering fields: Analog and Digital electronics, Control and signal processing, Programming and simulation | Technology brands: MITSUBISHI (MELFA software and manipulator RV 3SQB), Solidworks (Image conversion to coordinates), MATLAB (Camera tracking) | Keywords: Camera tracking, Trajectory planning, Mitsubishi RV 3SQB, Manipulator programming
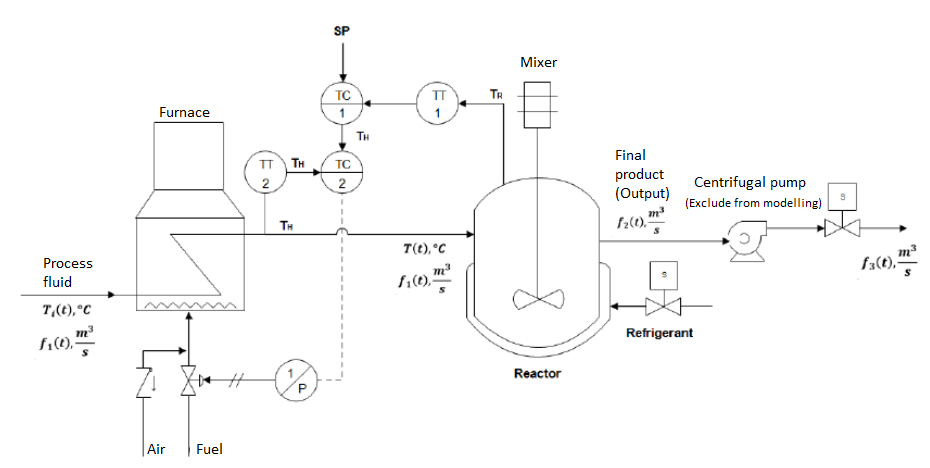

Year: 2018 | Engineering fields: Analog and Digital electronics, Control and signal processing, Programming and simulation, Thermodynamics | Technology brands: SIEMENS (PLC S7-1500 , Temperature Sensor PT100, Speed Drive Micromaster 440) | Keywords: Oil refining, SCADA systems, Remote supervision WinCC, Mechatronics modelling, PID Siemens PLC, Temperature control Siemens
Important documentation:
Siemens PID Module for PLC S7-1500
Siemens Speed Drive Micromaster 440 Manual
Siemens PT100 Temperature sensor Datasheet
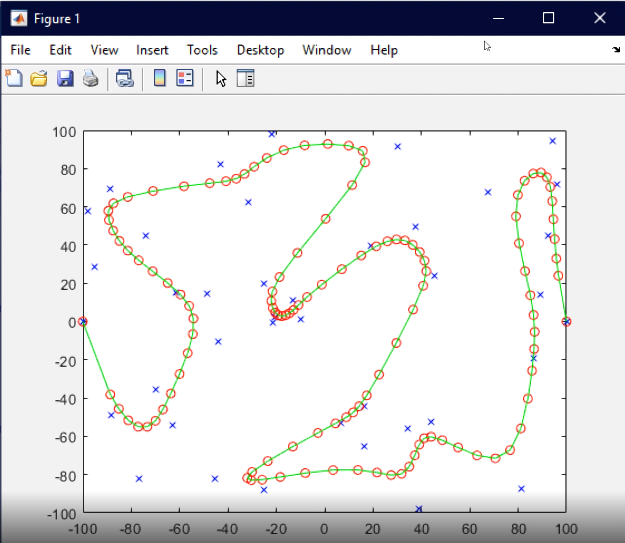
Year: 2018 | Engineering fields: Control and signal processing, Programming and simulation | Technology brands: MATLAB (Programming IDE) | Keywords: Self-Organizing map, Kohonen, Weights, Neural Network, Back-Propagation
Year: 2018 | Engineering fields: Programming and simulation, Dynamics | Technology brands: MATLAB (Programming IDE) , XFLR5 (Aerodynamics software) | Keywords: Lift coefficient, Aerodynamics, VLM, Vortex Lattice Method, Wing panels